- EUR-LIVE
- eur-live@u-pec.fr
Oliver Bischof et José Américo Freitas, enseignants de l'EUR LIVE, sont co-auteurs de cet article.
ils publient cette étude prometteuse sur les maladies liées au vieillissement dans le numéro du 19 février 2024 de la revue Nature Metabolism:
Accès à la revue en OPEN ACCESS ici
Abstract:
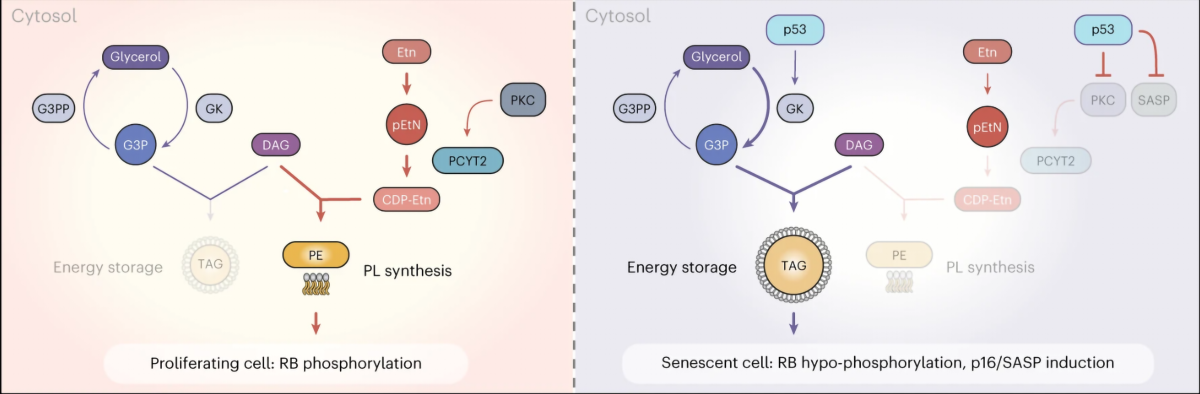
“Cellular senescence affects many physiological and pathological processes and is characterized by durable cell cycle arrest, an inflammatory secretory phenotype and metabolic reprogramming. Here, by using dynamic transcriptome and metabolome profiling in human fibroblasts with different subtypes of senescence, we show that a homoeostatic switch that results in glycerol-3-phosphate (G3P) and phosphoethanolamine (pEtN) accumulation links lipid metabolism to the senescence gene expression programme. Mechanistically, p53-dependent glycerol kinase activation and post-translational inactivation of phosphate cytidylyltransferase 2, ethanolamine regulate this metabolic switch, which promotes triglyceride accumulation in lipid droplets and induces the senescence gene expression programme. Mechanistically, p53-dependent glycerol kinase activation and post-translational inactivation of phosphate cytidylyltransferase 2, ethanolamine regulate this metabolic switch, which promotes triglyceride accumulation in lipid droplets and induces the senescence gene expression programme. Conversely, G3P phosphatase and ethanolamine-phosphate phospho-lyase-based scavenging of G3P and pEtN acts in a senomorphic way by reducing G3P and pEtN accumulation. Collectively, our study ties G3P and pEtN accumulation to controlling lipid droplet biogenesis and phospholipid flux in senescent cells, providing a potential therapeutic avenue for targeting senescence and related pathophysiology.”
Mise à jour le 4 août 2022